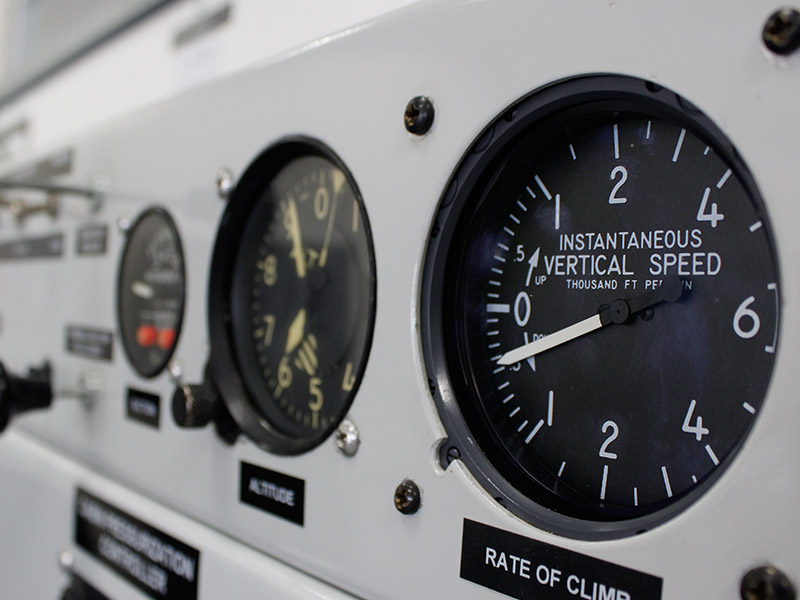

This workshop is used to provide the following classes: aircraft systems, cockpit instruments, aircraft structures, aerodynamics, multi-sensor systems, aircraft structure and properties, digital electronics, etc.
Among the available auxiliary equipment to teach these classes are: Digital engine training panel, Autopilot training panel, Pressurization system panel.
Students are trained on these training panels, basically to show them how these systems operate, and give them a more tangible idea of the aircraft systems operation.
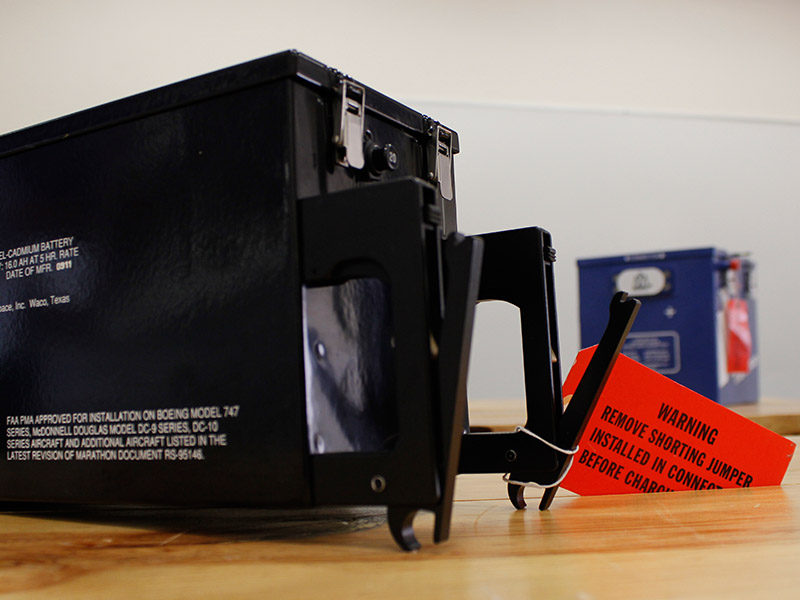

In this laboratory, students learn the process of charging and discharging aircraft batteries, using the Superseder III battery charger and different batteries from various manufacturers such as SAFT, among others. They also use aircraft batteries available in the French-Mexican Campus. There, students perform practices in order to ensure that the battery is capable of working on the aircraft as specified. These tests are important because battery performance will degrade during its normal use, being subject to continuous charging processes and to being left in storage. In addition, students learn about the different types of maintenance that a battery has gone through before being installed in an aircraft.
On the other hand, students can perform electricity practices to learn how to measure the different variables of a basic electrical circuit, such as electric current intensity and electrical voltage.
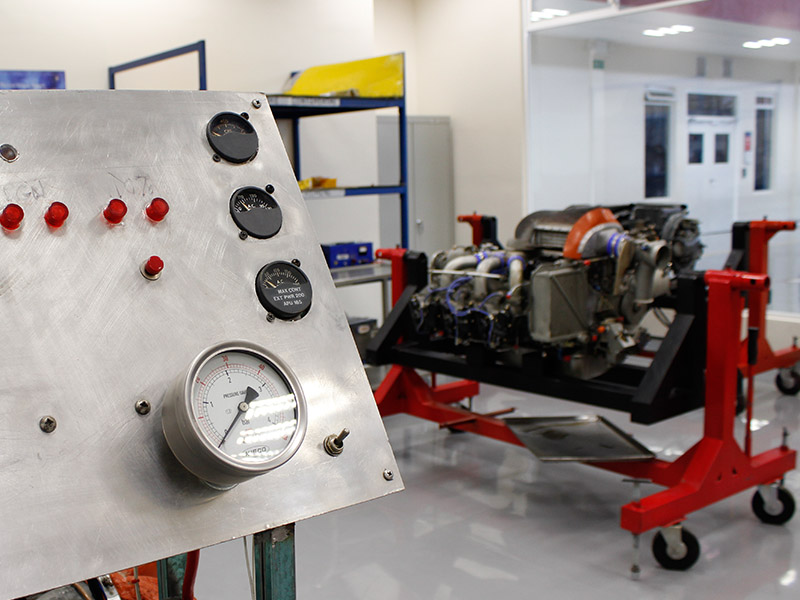

Students practice major service (Overhaul) in aviation engines, disassembly, inspection, repair and testing of engines and their components.
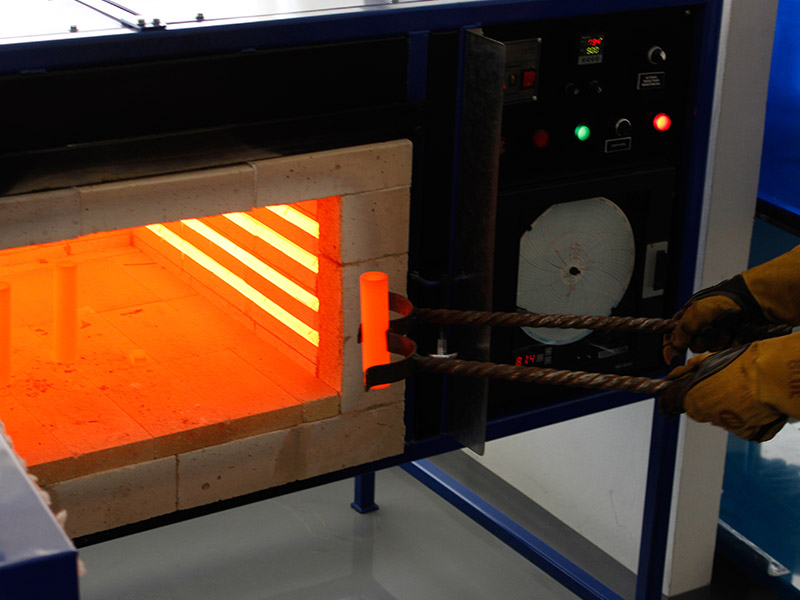
In the Thermal Processes and Welding Workshop, students use the welding stations to apply the knowledge acquired in the classroom in projects that require operations of joining metal materials, based on the welding techniques SMAW (Stick), GMAW (MIG), GTAW (TIG) and OAW (Oxyacetylene); Additionally, students learn about the equipment and accessories involved, the preparation of the material, safety measures and personal safety, and the evaluation of the welding acceptance criteria based on the parameters indicated in a WPS (Welding Procedure Specification).
Additionally, in this workshop, students make use of the heat treatment furnace to subject ceramic and metal materials to temperature changes by means of cooling curves, according to international standards, to modify their crystalline and metallurgical properties. The melting furnace is also used for manufacturing practices, such as Investment Casting, which require the pouring of metals in a liquid state, with a melting point below 950 ° C.
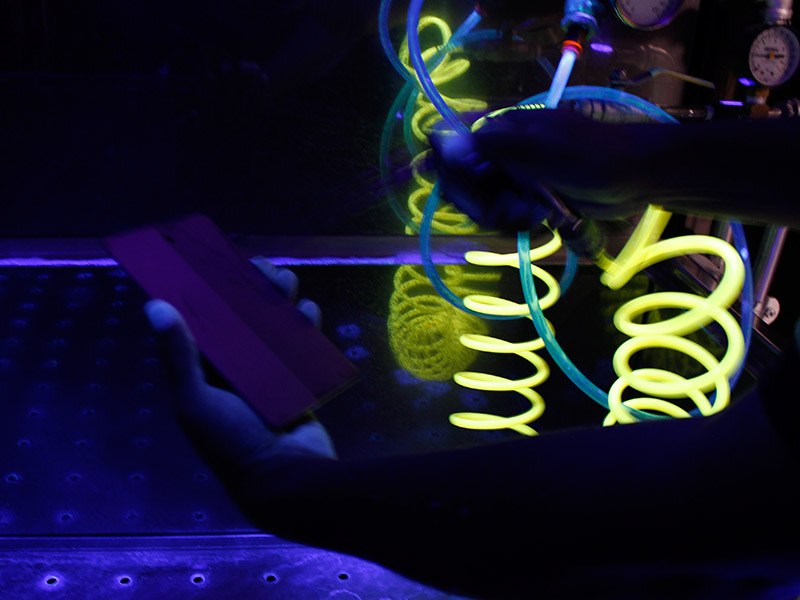

In the Penetrant Liquids Inspection Workshop, students use the line of penetrating liquids which carries out the cleaning of the piece, the application of the penetrating liquid, and the removal of the penetrating liquid in the cabin used for that purpose. They also use the oven to dry the piece, the developing cabin for the application of the developing powder, and finally, the respective inspection cabin for verification. All the mentioned above, to apply the acquired classroom knowledge regarding the steps that are followed to perform an inspection with penetrating liquids, to know the equipment and accessories, and to evaluate the acceptance criteria of a piece in accordance with the corresponding manuals.
Students use the worktables to perform visual inspection of components, to apply knowledge acquired in the classroom regarding dimensional inspection. They evaluate the acceptance criteria of a piece in accordance with the corresponding manuals. Students use the magnetic particle inspection machine, where they apply the acquired classroom knowledge regarding the steps that are followed to perform the aforementioned inspection, learn about the equipment and accessories, and evaluate the acceptance criteria of a piece according to the corresponding manuals.
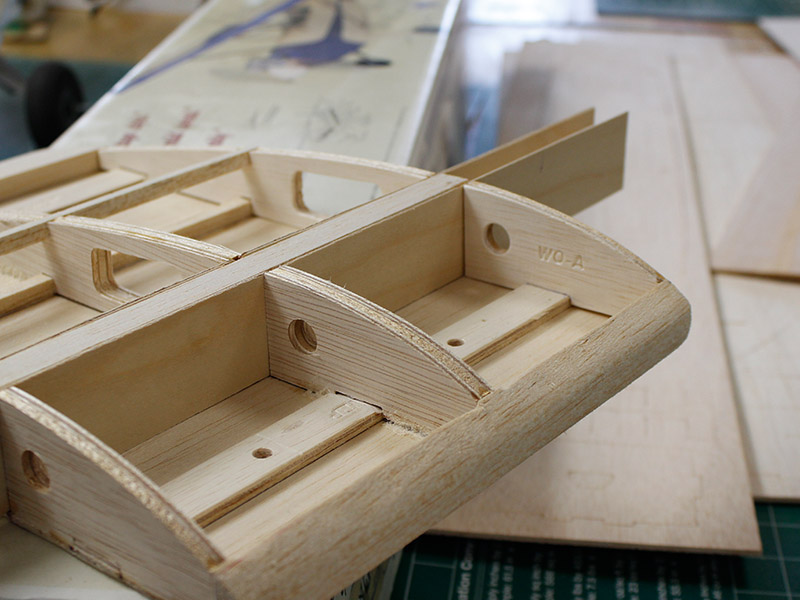

The activities carried out in the workshop consist of the manufacturing of unmanned aircraft, where students have the opportunity to apply the knowledge they acquired in their classes. Students design the UAS and then they carry out the manufacture of the vehicle using different tools and acquiring skills in the construction of prototypes.
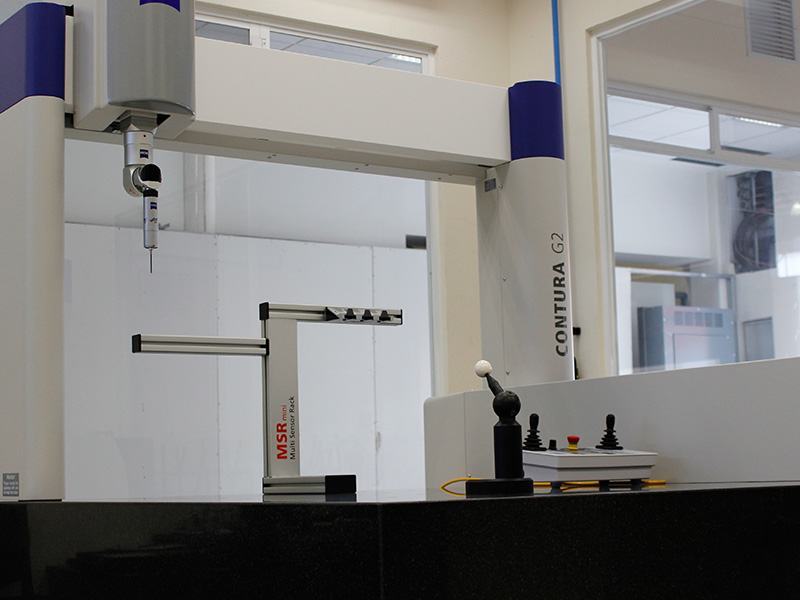

Students know and become familiar with the measuring instruments and most used practices in the aeronautical environment.
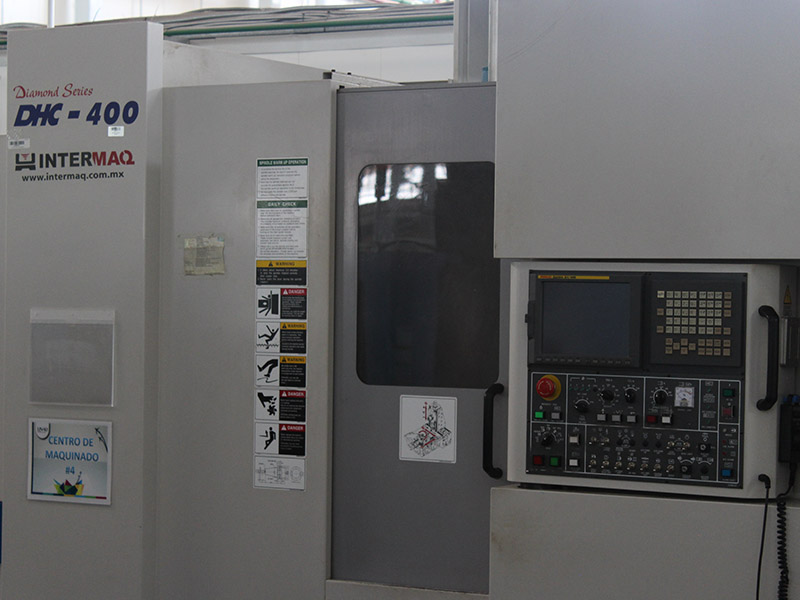

This laboratory is part of the area of intensive training programs, allowing the use of the machine 7, 3-axe Doosan CNC, aimed to be used during the TSU practices. There are conventional lathe and milling machines, used for demonstrations in TSU and engineering practices.

In this workshop, located on the ground floor of the Hangar of the French-Mexican Campus, students can carry out activities aimed to identify aircraft materials before intervening in their cleaning treatment, CPC and paint application; preparation of the fuselage and or components to be painted (wallpaper or masking); application of CPC (Corrosion Preventive Compound) to sub-assemblies and / or aircraft components; primer application to sub-assemblies and / or aircraft components; and the application of "enamel" or "polyurethane" paints to sub-assemblies and / or aircraft components.

This workshop is located next to the painting workshop. Here, students perform aircraft structure damage identification and assessment practices, manufacturing of structural assemblies and sheet metal and composite materials parts, repairing of damages using sheet metal and composite materials in structural assemblies. Pieces are sent the Aeronautical Painting workshop if needed.

Carretera Estatal 200 Querétaro – Tequisquiapan No. 22154
Col. Parque Aeroespacial de Querétaro.
Colón, Querétaro. México
C.P. 76278
Teléfono: (442) 101 66 00
2022 | Universidad Aeronáutica en Querétaro